Mongolia’s Khuvsgul Lake National Park has been added to UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves. The lake is located near the Russian border in the Northern Mongolian province of Khuvsgul.

UNESCO has approved the creation of 11 new biosphere reserves in nine countries, including three new countries: Chad, Georgia, and Zambia. In addition, two existing biosphere reserves in Spain have been expanded. The World Network of Biosphere Reserves now has 738 sites in 134 countries, thanks to the new designations.
This article will also be very useful for those preparing for UPSC, SSC, CUET, and other exams because many questions about biosphere reserves are asked in competitive exams.
You should know that Biosphere reserves are not only for the protection of flora and fauna but also for human communities. In today’s post, we are going to provide all the necessary details related to the Biosphere Reserves in India.
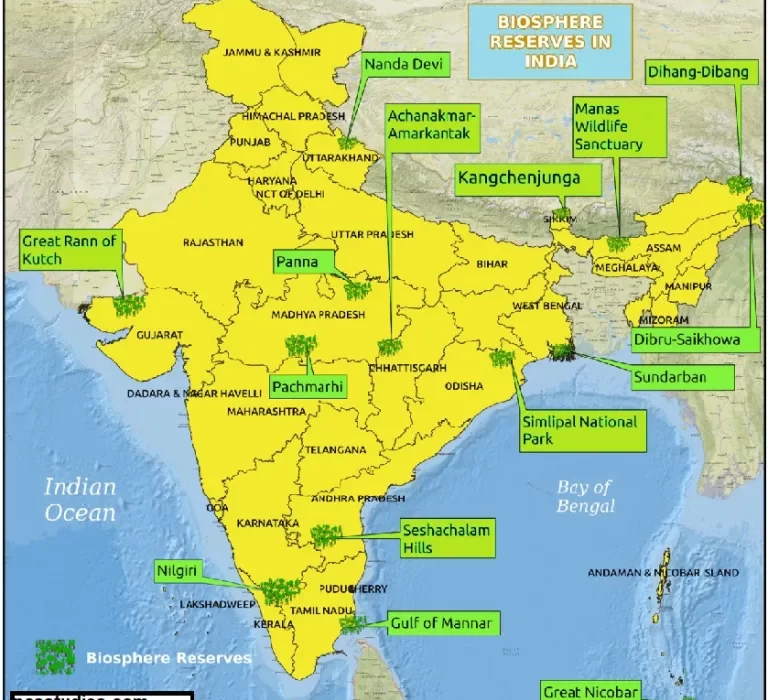
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
As mentioned above there are 18 Biosphere reserves in India. The list of the same is given below.
| Name of the Biosphere Reserves | State | Year | Area (sqkm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka | 1986 | 5520 |
| Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | Uttarakhand | 1988 | 5860 |
| Gulf of Mannar | Tamil Nadu | 1989 | 10500 |
| Nokrek | Meghalaya | 1988 | 820 |
| Sundarbans | West Bengal | 1989 | 9630 |
| Manas | Assam | 1989 | 2837 |
| Simlipal | Odisha | 1994 | 4374 |
| Dihang-Dibang | Arunachal Pradesh | 1998 | 5112 |
| Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh | 1999 | 4982 |
| Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh | 2005 | 3835 |
| Great Rann of Kutch | Gujarat | 2008 | 12454 |
| Cold Desert | Himachal Pradesh | 2009 | 7770 |
| Khangchendzonga National Park | Sikkim | 2000 | 2620 |
| Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve | Kerala, Tamil Nadu | 2001 | 3500 |
| Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 1989 | 885 |
| Dibru-Saikhowa | Assam | 1997 | 765 |
| Seshachalam Hills | Andhra Pradesh | 2010 | 475 |
| Panna | Madhya Pradesh | 2011 | 2999 |

List of biosphere reserve of India are recognized by UNESCO: International Status of Biosphere Reserves (BR)
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves includes 12 of the 18 biosphere reserves listed by the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme. The following is a list of UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserves in India in 2022.
Criteria for BR designation
- A site that contains an effectively protected and minimally disturbed core area of conservation value.
- The core area should be representative of a bio-geographical unit and large enough to support viable populations from all trophic levels in the ecosystem.
- The management authority to ensure local community involvement/cooperation in bringing a variety of knowledge and experiences to link biodiversity conservation and socioeconomic development while managing and containing conflicts.
- Potential areas for the preservation of traditional tribal or rural ways of life for the harmonious use of the environment
Structure and functions of the BR Biosphere Reserves are divided into three interconnected zones:
- Core Zone: The core zone must provide suitable habitat for a diverse range of plant and animal species, including higher order predators, and may contain endemism centres. Core areas frequently conserve the wild relatives of economically important species and also serve as important genetic reservoirs of exceptional scientific interest. A core zone is a National Park or Sanctuary that is protected or regulated primarily under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972. While acknowledging that perturbation is a component of ecosystem functioning, the core zone must be kept free of external human pressures.
- Buffer Zone: The buffer zone adjoins or surrounds the core zone, and uses and activities are managed in this area to help protect the core zone in its natural state. These uses and activities include restoration, demonstration sites for increasing the value of the resources, limited recreation, tourism, fishing, grazing, and so on, all of which are permitted to reduce the impact on the core zone. Research and educational activities will be promoted. Human activities, if natural within BR, are likely to continue as long as they do not harm ecological diversity.
- Transition Zone: A biosphere reserve’s transition zone is its most remote location. This is a zone of cooperation where conservation knowledge and management skills are applied and uses are managed in accordance with the purpose of the biosphere reserve. This includes the region’s settlements, crop lands, managed forests, and areas for intensive recreation, as well as other economic uses.
Biosphere conservation
India is a signatory to the landscape approach backed by the UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) programme, which serves as the guiding force behind the Biosphere Reserve Program. The Government of India has been operating a programme known as the Biosphere Reserve since 1986, in which financial support is given to the states of the North Eastern Region and the three Himalayan states in a ratio of 90:10 and to other states in a ratio of 60:40 for the upkeep, development, and improvement of specific items. The Management Action Plan is created by the State Government and is authorised and followed by the Central MAB Committee.
| Name of the Biosphere Reserves | Location | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | Part of Waynad, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Mudumalai, Nilambur, Silent Valley | 2000 |
| Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve | Indian part of Gulf of Mannar extending from Rameswaram island in the north to Kanyakumari in the south of Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka | 2001 |
| Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve | Part of delta of Ganges and Brahmaputra river system | 2001 |
| Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | Parts of Chamoli District, Pithoragarh District & Bageshwar District | 2004 |
| Nokrek Biosphere Reserve | In west Garo Hills | 2009 |
| Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Parts of Betul District, Hoshangabad District and Chhindwara District | 2009 |
| Simlipal Biosphere Reserve | Part of Mayurbhanj district | 2009 |
| Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | Southernmost of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 2013 |
| Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | Part of Annupur, Dindori and Bilaspur districts | 2012 |
| Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve | Neyyar, Peppara and Shenduruny Wildlife Sanctuary and their adjoining areas | 2016 |
| Khangchendzonga National Park | Parts of Kangchenjunga | 2018 |
| Panna Biosphere Reserve | Part of Panna and Chhattarpur districts in Madhya Pradesh | 2020 |
Potential Biosphere Reserves in India
The Ministry of Forests and Environment has identified the following potential sites for Biosphere Reserves:
- Abujmarh – Chhattisgarh
- Andaman and Nicobar – North Islands
- Chintapalli – Visakhapatnam Andhra Pradesh
- Kanha – Madhya Pradesh
- Kovalam – Kerala
- Lakshadweep Islands – Lakshadweep
- Little Rann of Kutch – Gujarat
- Phawngpui (Blue Mountain) – Mizoram
- Namdapha – Arunachal Pradesh
- Singhbhum – Jharkhand
- Tawang and West Kameng – Arunachal Pradesh
- Thar Desert – Rajasthan
- Tadoba National Park and Sanjay Gandhi National Park – Maharashtra
FAQ for Competitive Exams
Largest Biosphere Reserve in India?
Answer: Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat is the largest Biosphere Reserve in India.
Smallest Biosphere Reserve in India?
Answer: Dibru – Saikhowa in Assam is the smallest Biosphere Reserve in India.
First Biosphere Reserve in India?
Answer: The first Biosphere Reserve in India is the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (part of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka).
Difference between a national park and a biosphere reserve?
National parks are created to protect public lands from industrialization, human exploitation, and pollution. A biosphere reserve, on the other hand, is a designated area for the conservation of the biosphere’s resources and the improvement of man’s relationship with the environment.
Distribution of Biosphere reserves across the world?
The distribution of Biosphere reserves across the world’s continents is shown below.
- 85 reserves in 31 countries in Africa
- 33 reserves in 12 countries in the Arab States
- 157 reserves in 24 countries in Asia and the Pacific
- 302 reserves in 38 countries in Europe and North America
- 130 reserves in 21 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean.

